Published the 01/06/2023
Hydrogen is a versatile and valuable resource for various industries, including chemical, metallurgy, and glass manufacturing. However, 95% of the hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels, known as fossil hydrogen or grey hydrogen, and has a significant environmental impact, emitting large amounts of greenhouse gases.
In contrast, renewable hydrogen, or green hydrogen, produced using renewable energy sources, offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil hydrogen.
In this article, we will explore the benefits of renewable hydrogen in industrial applications and how it can help reduce CO2 emissions.
The Carbon Footprint of Fossil Hydrogen
Fossil hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels, primarily natural gas through a process known as steam methane reforming (SMR), but also in some cases naphtha (from oil refining) or coke through gasification. These processes emit large amounts of carbon dioxide, contributing significantly to global carbon emissions.
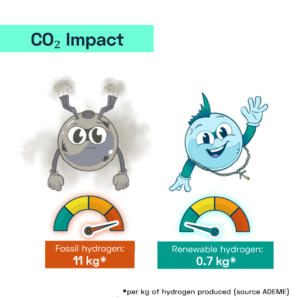
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions associated with fossil hydrogen production amount to around 10-11 kg of CO2 per kg of hydrogen produced. This currently represents over 900 million tons of CO2 per year or around 10% of the world’s industrial C02 emissions!
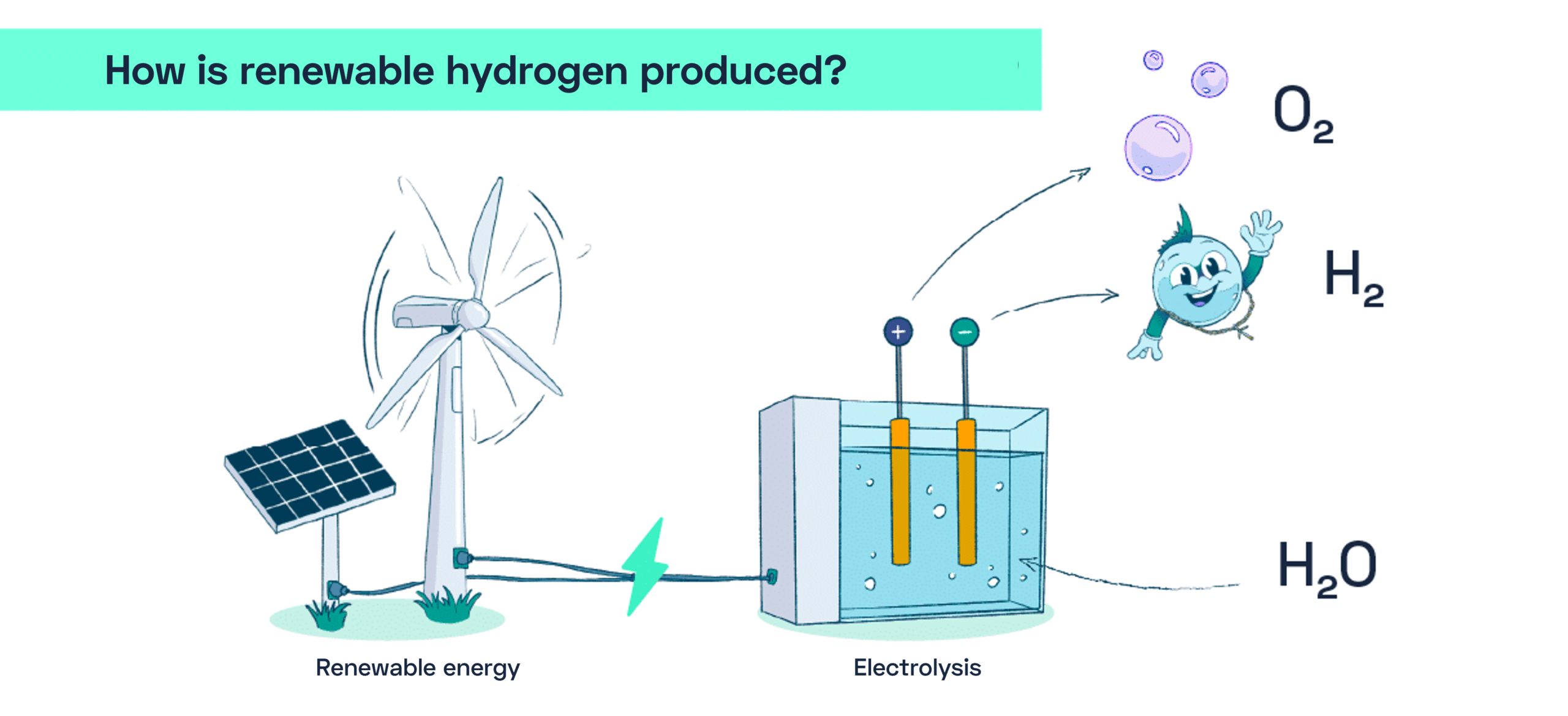
Renewable Hydrogen: A Sustainable Solution
Renewable hydrogen is produced from renewable energy sources such as hydroelectricity, wind power, and solar energy, using a process known as water electrolysis. This process splits the water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity.
The use of renewable hydrogen in industrial processes can significantly reduce carbon emissions, making it a sustainable, environmentally friendly alternative to fossil hydrogen.
Chemical industry
In the chemical industry, renewable hydrogen can be used to replace fossil hydrogen as a raw material to produce fertilizers, plastics and other products, as well as ingredients for the pharmaceutical and food industries. Hydrogenation is an essential process widely used in the chemical industry, involving the addition of hydrogen to unsaturated compounds, transforming them into saturated equivalents. This reaction plays a major role in modifying and improving the properties of chemical products for a variety of uses.
Metallurgy
In the metal industry, hydrogen finds diverse applications, ranging from metal production and steel annealing to heat treatment, welding, cutting, and surface finishing. Its unique properties and reactivity contribute to enhancing metal properties, ensuring the production of high-quality metal products across various industrial sectors. The use of renewable hydrogen in the metallurgical industry can reduce carbon emissions, for instance in steel production, where blast furnaces are one of the largest sources of industrial emissions.
Glass industry
Hydrogen also plays an important role in various processes in the glass industry. From glass melting and forming to coating, polishing, and cleaning, to the controlled atmosphere of the tin bath for flat glass production, hydrogen’s unique properties contribute to energy efficiency, improved product quality, and the sustainability of glass production. By replacing fossil hydrogen with renewable hydrogen, the glass industry can achieve cleaner production.
In conclusion
The use of renewable hydrogen for applications, such as chemical, metallurgy, and glass manufacturing can significantly reduce carbon emissions and help create a sustainable future for the industry. With increasing investments in renewable hydrogen infrastructure and technology, a hydrogen-based economy is becoming more and more feasible.
By embracing renewable hydrogen, we can pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable future for industry and the environment.
Would you like to make your hydrogen project a reality?
Contact our hydrogen expert